What are the Types of Inheritance in Java? Examples andTips to Master Inheritance
Inheritance in OOP (Object Oriented programming), Java is a mechanism that allows the creation of a new class by reusing an existing class. For example, you can create a class, ‘Rose,’ based upon an existing class, ‘Flower.’ So, in the ‘Rose’ class, you can add
like color and scent that can be derived from the ‘Flower’ class. As a result, it will help you save time and effort without having to write the same code several times.
Now, there are different types of inheritance in Java that incorporate unique concepts. However, the core concept remains the same. That is the parent and child class links in such a way that they pass the methods through different generations or child classes.
In this article, you will learn each of the types of inheritance in Java in detail and know how to master them.

Table Of Content
Inheritance and its Types in Java
Benefits of Different Types of Inheritance in Java
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
Inheritance and its Types in Java
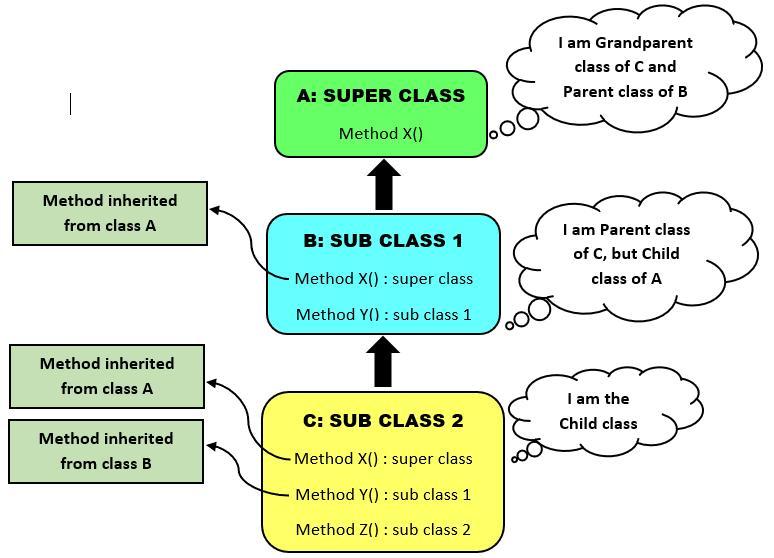
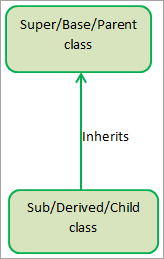
Inheritance in Java is the technique through which an object gets all the behaviors and properties of its parent object. As a result, you can build a new class based on an existing class. The new class is known as the child or sub-class, whereas the existing class is known as the parent or superclass. The child class can access and reuse all the members, including methods and fields of the parent class. The inheritance represents the ‘is-a’ relationship that indicates the parent-child relationship.
Here, you will learn about the five types of inheritance in Java and their examples.
Single Inheritance in Java
Single inheritance is one of the basic types of inheritance in Java that requires one parent class and one child class. Through this inheritance, you can extend one class from another by reusing the methods and fields of the parent class. It makes your code much easier to understand and helps update it.
For example, let your Animal class hold the attribute like eating fish. Now, a new class named Cat automatically receives this attribute using the single inheritance mechanism. This way, the child class Cat carries the attributes of the parent class Animal without the requirement of complex maintenance procedures.
Also, the Cat class has its own attribute, meow that is not inherited from the parent class.
class Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println(“Eating”);}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
void meow(){System.out.println(“Meowing”);}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Cat c=new Cat();
c.meow();
c.eat();
}}
Benefits of Different Types of Inheritance in Java
You can gain these facilities by implementing different types of inheritance in Java –
Code reusability: The first and foremost benefit you can gain is code reusability. The inheritance mechanism helps you avoid code redundancy.
Flexibility: Types of inheritance in Java employ structural and hierarchical ways to organize your code. As a result, your code looks clean and easily represents the relationship between different classes.
Easy to maintain: The subclasses achieve the features of the superclass by inheritance. Thus, if you change the superclass, the subclasses will also reflect those changes. This makes your code easier to maintain.
Simplified design: As you can extend the classes with the types of inheritance in Java, you don’t need to write the code from scratch. So, it helps to avoid unnecessary complications.
Conclusion
You can acquire advanced programming knowledge by understanding the concept of numerous types of inheritance in Java. It supports levelling up your skills and remains competitive in the job market. Self-learning and practicing are great strategies for boosting your expertise in the types of inheritance in Java.
However, you should opt for professional computer science courses like the Executive Programme in full stack web development to drive your career on the right path. This course will provide you with more exposure to real-world applications through which you can understand the concepts of inheritance better!