
Operators in C Language: Types and Examples
In the realm of programming, operators play a key role in performing operations on variables and values. And, when it comes to the C language – one of the most popular and widely used programming languages—understanding the role of these operators is crucial to writing efficient and effective code.
Operators in C are special symbols or keywords that instruct the compiler to perform specific operations. They are used for versatile purposes like arithmetic calculations, determining relations, decision-making, calculating memory size, and more.
The following write-up will explore different types of operators in the C language, their functionalities, and syntaxes for a detailed understanding.
Table Of Content
Types of Operators in C
Other Types of Operators in C
Significance of Operators in C
Unlocking Tech Potential with a Comprehensive BCA Program
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
Types of Operators in C
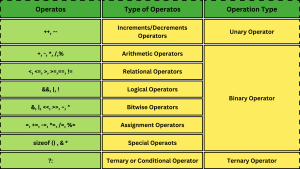
*logicmojo.com
Other Types of Operators in C
Significance of Operators in C
Here is why the operators in C are necessary –
- Perform mathematical calculations: The arithmetic operators in C help to perform the basic mathematical calculations such as addition, multiplication, subtraction, and division.
- Maintain the program’s flow: The logical operators in C help in the decision-making process of conditional statements. This way, they maintain the program’s flow and reduce code redundancy.
- Improve readability: The ternary operators make the conditional logic readable and concise.
- Handle pointers and memory: Special operators like * and & are mandatory to efficiently handle operations regarding pointers, manipulation, and memory allocation.
- Simplify code: The operators like arithmetic and assignment simplify the code by reducing the necessity of writing longer expressions.

*logicmojo.com
Unlocking Tech Potential with a Comprehensive BCA Program
C programming is a fundamental topic of computer science. It also provides the core concepts that help individuals to learn other programming languages. So, individuals interested in the C programming language should take a profession certification course that helps in their career growth. For example, they can take the Online BCA Programme – Manipal University Jaipur.
The course not only covers C programming but also covers advanced technologies like cloud technology, Big Data, machine learning, DBMS, etc. Apart from these, the course also guides the students to gain knowledge about financial accounting and management, personality development, and building impactful communication skills. These ways, the program supports the students to get ready for the dynamic world of the corporate sector.
Conclusion
So, this guide covered all the major operators in C. The operators are the core concepts of any programming language, and without them, the code can’t stand at all. Thus, students need extensive knowledge about the operators to efficiently write code in any programming language and improve their career prospects.

